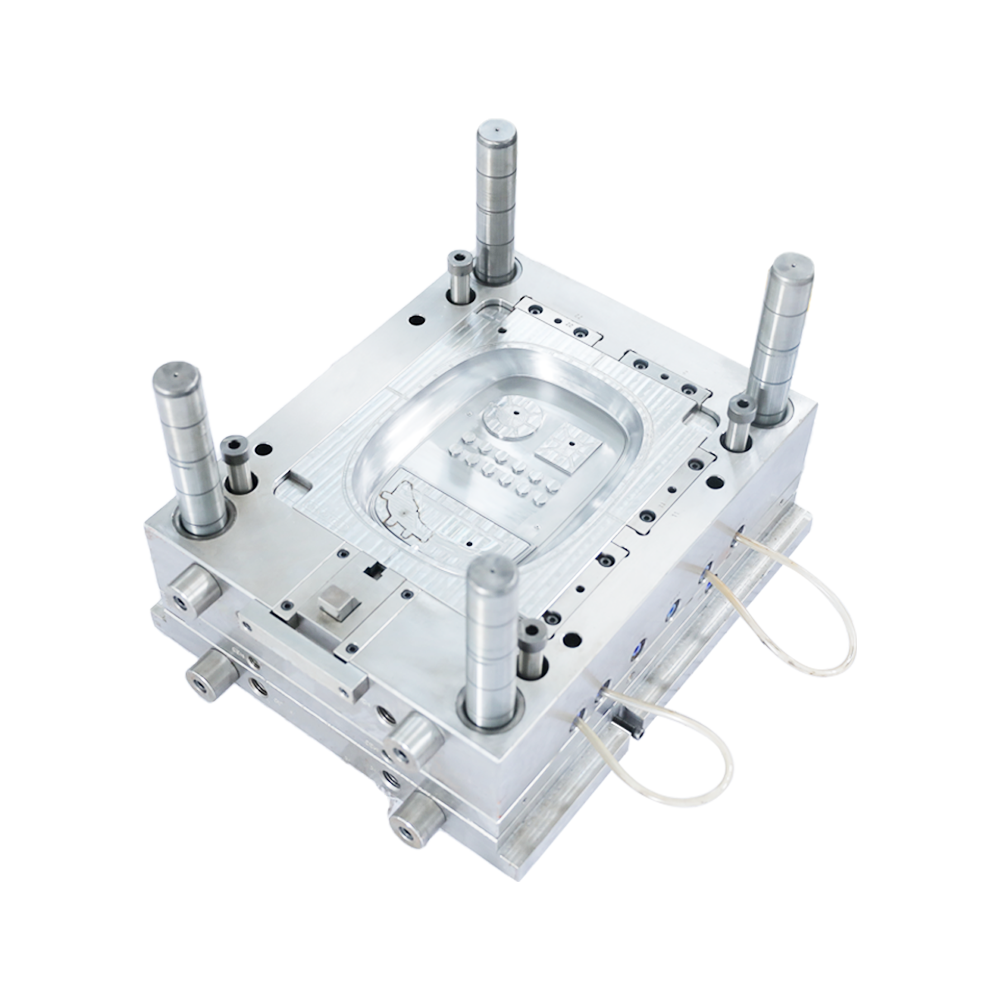
When making parts for a car, the best way to create quality products is to use injection molding. Automotive parts have high quality and safety requirements, and injection molding is an irreplaceable advantage in the production process. Injection molding is an ideal solution for manufacturing plastic structural components. It can also be used for parts that are not usually injection molded, such as fluid handling plastic structural components.
Plastic injection molding
While metal and steel are traditionally associated with the automotive industry, plastic is becoming increasingly important in car manufacturing. Plastics are stronger and more durable than metal, and have many other advantages. Moreover, consumers today have a different set of expectations for their vehicles, and plastic injection molding is an excellent way to meet these expectations.
Injection molding is an excellent option for automakers who want to manufacture high-quality parts at low costs. It allows companies to create intricate and complex designs with greater ease. The process also scales well for mass production and allows manufacturers to run tens of thousands of items through a mold at once.
Injection molding uses high-pressure injection to shape polymer into desired shapes. Depending on the application, moulds can have single or multiple cavities. A single cavity mould can produce identical parts while multiple cavities can produce parts with different geometries. Tool steel moulds are typically used for injection molding, but stainless steel or aluminium moulds are also popular options.
Die-casting
Die-casting is a process used in making components used in autos and other vehicles. The production of these components is highly dependent on the materials used. Some of these materials are softer than others. For example, cast iron cannot sustain high pressures and it requires a special die. This type of die is expensive and requires significant start-up expenses.
Another material commonly used in auto parts is magnesium, a lightweight metal with excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Because magnesium is naturally occurring, its abundance makes it an environmentally friendly option. Moreover, it can be recycled without leaving any traces behind. Die-casting for automobile parts can be done using cold chamber or hot chamber die-casting machines. Which process you choose will depend on the size and complexity of the parts.
Some key players in the market include Altizon Inc., Endurance Technologies Ltd., and Georg Fischer Limited. These companies are involved in the production of complex die-cast parts and system components. Some of these companies also produce automotive-related machinery.
Overmolding
Overmolding is a process that involves combining different materials to form an automotive part. It is important to choose the correct material for a specific application. The adhesion between the material and substrate depends on three factors: surface texture, resin compatibility and surface treatment. A custom injection molder can guide you through these considerations and choose the right material for your application.
Overmolded parts are stronger and more durable than non-moulded ones. This manufacturing process also eliminates the need for secondary operations, extra adhesives, and fasteners. The process saves a great deal of time and money, and is also highly convenient. In addition, overmolded parts have a protective layer of thermoplastic material that is flexible and durable.
Overmolding can also help improve fuel efficiency and reduce vehicle weight. The process of replacing metal parts with plastic is one of the most efficient ways to make vehicles lighter. However, replacing heavy metal parts with plastic can be challenging, especially when they need to have high strength. Heavy metal parts require more expensive production processes and increase vehicle weight. Using overmolding, however, can solve this problem.
Overmolding with polypropylene
When overmolding with polypropylene, there are a few factors that must be considered to ensure that the end result meets all design requirements. The material's chemical and physical properties must match those of the substrate. In other words, the material cannot be molded directly onto stainless steel or a similar substrate.
To get the best results from the overmolding process, you must first understand the function of the part. In most cases, the primary function is to provide a proper seal. However, it is also important to consider how the part will be exposed to UV light and harsh chemicals. Once you know where the part will be used, you can select a material that will not be damaged by harsh chemicals or UV light.
To determine the ideal temperature range for overmolding with polypropylene, we first conducted a numerical simulation. In this simulation, we simulated a two-step molding process and determined the optimum mold temperature. This temperature was chosen so that the temperature gradients along the melt flow path would be the least. This information was then used to make design modifications.



 ��������
��������