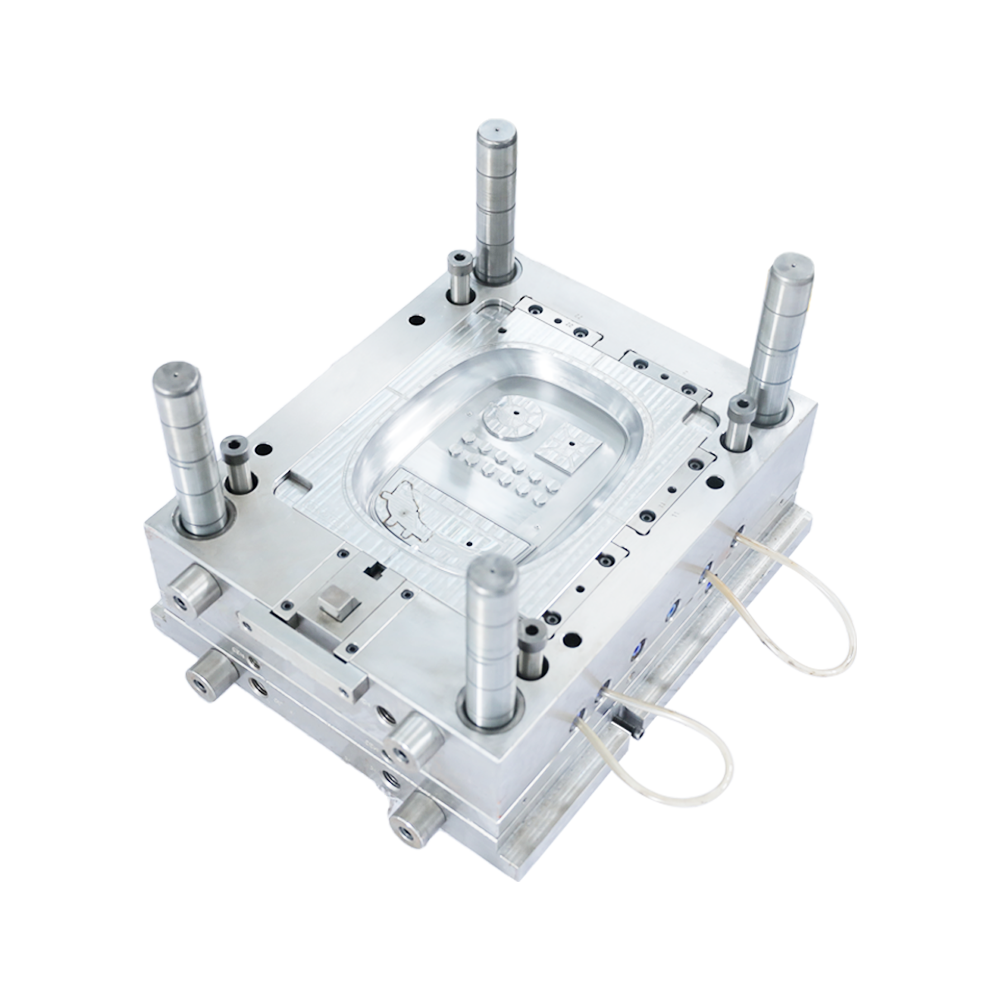
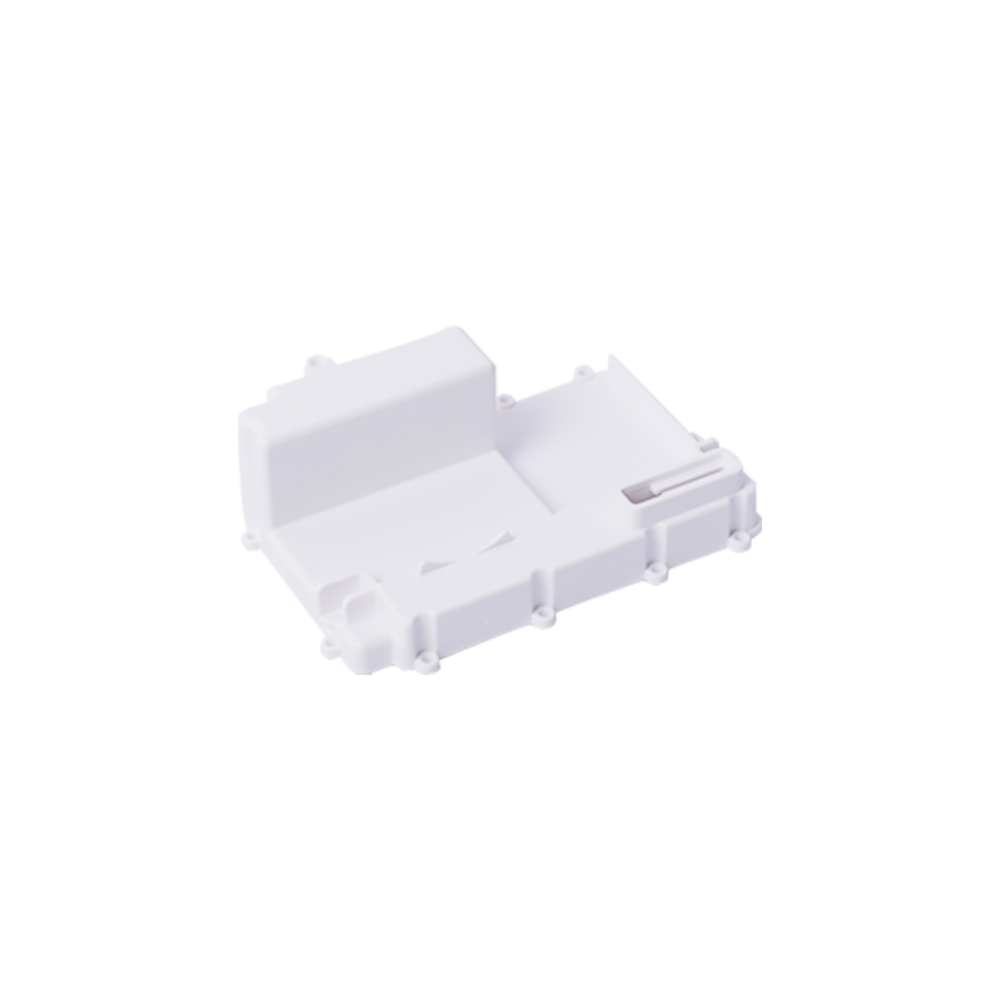
Due to different stamping processes and different working conditions, there are many reasons for the bursting of stamping dies, and the life of dies of different materials is often different. To this end, the basic requirements for the material of the working parts of the die are put forward:
(1) The performance of the material should have high hardness (58-64HRC) and high strength, as well as high wear resistance and sufficient toughness, small heat treatment deformation, and certain hot hardness;
(2) The process performance is good. The processing and manufacturing process of the working parts of the die is generally complicated, therefore, it must have adaptability to various processing techniques, such as forgeability, machinability, hardenability, hardenability, quenching crack sensitivity and grinding workability, etc. .
Heat treatment: deformation caused by improper quenching and tempering process
Practice has proved that the thermal processing quality of the mold has a great influence on the performance and service life of the mold. According to the analysis and statistics of the reasons for the failure of the mold, the "accidents" of mold failure caused by improper heat treatment account for more than 40%.
(1) Forging process: This is an important link in the manufacturing process of mold working parts. For molds of high alloy tool steel, technical requirements are usually put forward for metallographic structures such as material carbide distribution.
(2) Preliminary heat treatment: Depending on the material and requirements of the working parts of the mold, preliminary heat treatment processes such as annealing, normalizing or quenching and tempering should be used to improve the structure, eliminate the structural defects of the forging blank, and improve the processing technology. After proper preparatory heat treatment, the high carbon alloy die steel can eliminate the reticulated secondary cementite or chain carbide, make the carbide spheroidized and refined, and promote the uniformity of carbide distribution, which is conducive to ensuring quenching and tempering. quality, improve mold life.
(3) Quenching and tempering: This is the key link in the heat treatment of the mold. If overheating occurs during quenching and heating, it will not only cause greater brittleness of the workpiece, but also easily cause deformation and cracking during cooling, which will seriously affect the life of the mold. When the die is quenched and heated, special attention should be paid to preventing oxidation and decarburization, and the heat treatment process specification should be strictly controlled. When conditions permit, vacuum heat treatment can be used. After quenching, it should be tempered in time, and different tempering processes should be adopted according to technical requirements.
(4) Stress relief annealing: After rough machining, the mold working parts should be subjected to stress relief annealing treatment. The purpose is to eliminate the internal stress caused by rough machining, so as to avoid excessive deformation and cracks during quenching. For molds with high precision requirements, stress relief tempering is required after grinding or electrical machining, which is conducive to stabilizing mold accuracy and improving service life.
 +86-15995701933
+86-15995701933 [email protected]
[email protected]- OEM Plastic Mould Manufacturers

 ��������
��������