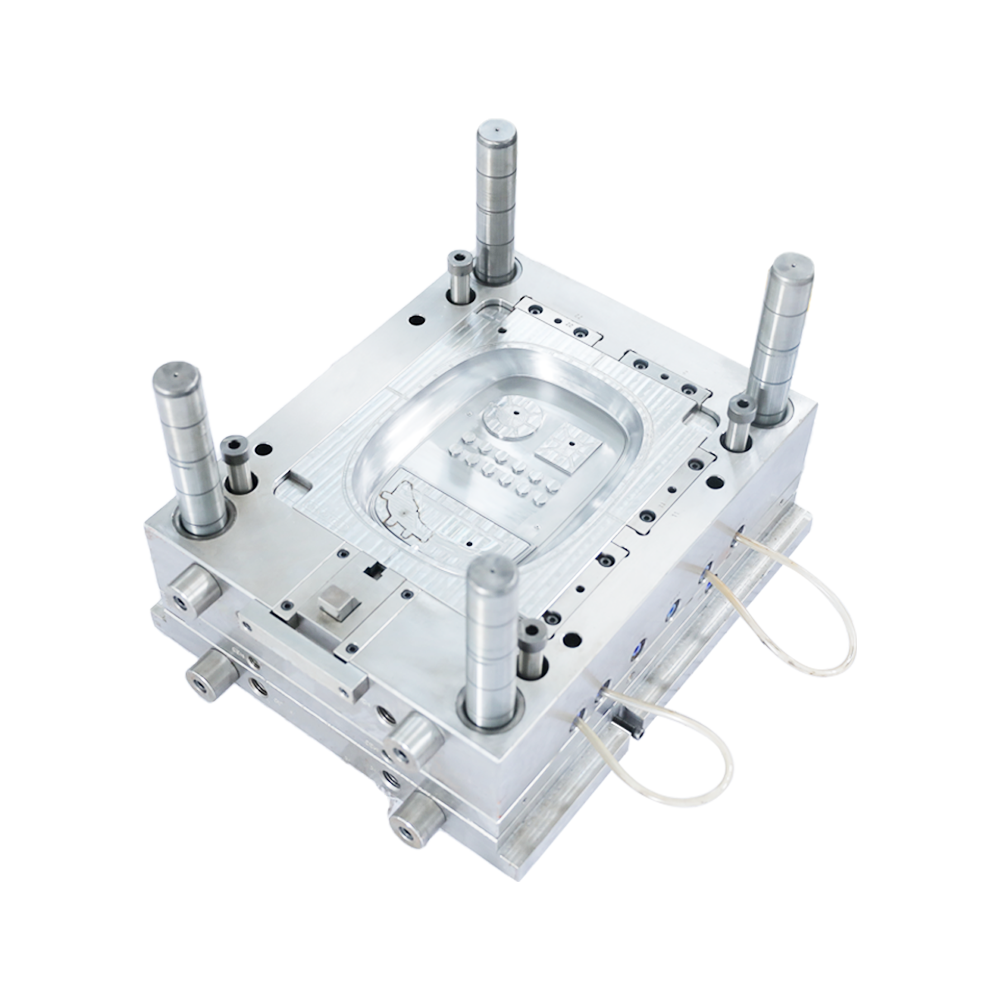
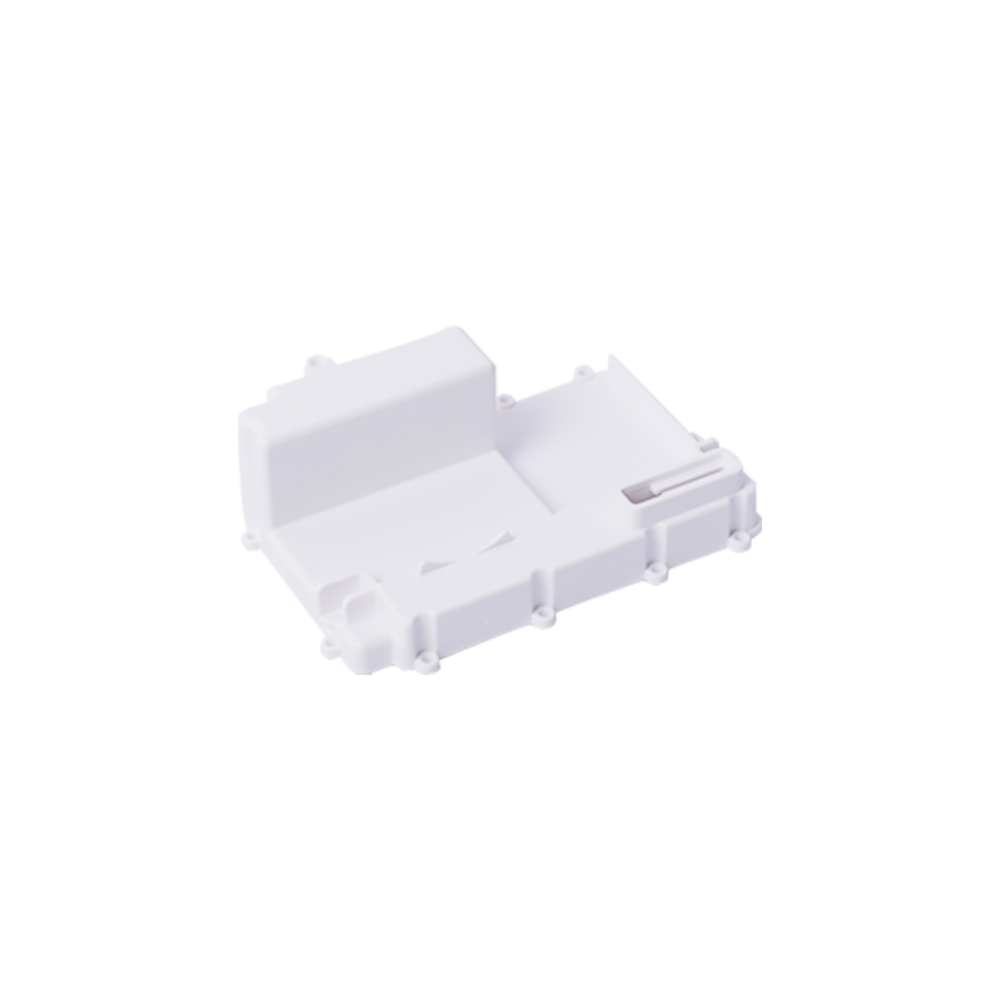
A medical equipment mould is a crucial component of a variety of medical devices. The process of mould making is not simple, however. It must be performed in a controlled environment. There are several factors to consider, including product safety, quality, and timeliness. These factors should be taken into account to ensure that your medical equipment mould is of the highest possible standard.
Class III medical devices
The strictest regulatory standards in the industry apply to class III medical equipment, including implantable pacemakers, continuous glucose monitors, and other such devices. Typically, moulding for these products is done in cleanrooms that prevent the contamination of the components through airborne particulate matter. But, the cleanroom requirements can be prohibitively expensive, and the process also requires skilled personnel to meet the necessary quality standards. Fortunately, there are a number of ways to maintain quality standards.
The manufacturing facility must meet certain standards, including the ISO 13485:2003 standard. It must also adhere to biocompatibility regulations, including USP Class VI biocompatibility, and ISO 10993:2003. These standards include a detailed list of control procedures, including risk management and lot traceability. The FDA has classified medical devices into three classes according to the level of risk associated with each one. Molding for these devices is done using post-processing operations that can help ensure continuous compliance.
Medical equipment moulds are often quite complex, with intricate details that should not be overlooked. From cardiac EKG machines to IV pumps, surgical carts to housings for oxygen and IV pumps, this type of moulding requires a highly skilled engineering team to ensure that each part meets the standards set by the FDA. By applying the highest standards, manufacturers can ensure the safety of their products and minimize the risk of contamination. They also want to ensure their products are manufactured as cleanly as possible to minimize any damage they can cause to patients.
Class II medical devices
When looking for a moulder, consider the following: environment, processes, and quality. Are you able to transition seamlessly from prototype to initial production and from low-volume to high-volume production? Can you maintain quality standards and customer satisfaction during this transition? These are the four E's that are most important for medical molders. Read on to learn more about the specific challenges facing the industry. Then, select a moulder who is capable of meeting these challenges.
Cleanroom environment: When a molder uses a cleanroom, the process is highly regulated. Cleanrooms are important for producing Class II medical equipment because they protect against airborne particles. Injection molding processes should be ISO 7 or ISO 8, which means a minimum of 10,000 pollution particles per cubic meter. ISO 8 cleanrooms are also the most stringent. Cleanrooms are also necessary for manufacturing Class II medical devices.
Lubrizol Life Science Health: A contract molder that specializes in scientific injection molding has the knowledge and expertise to produce high-quality products. This includes everything from material selection to clean room packaging. The company started out as a small molder with limited resources and has expanded into one of the largest medical equipment parts manufacturers in the country. Its extensive capabilities and experience in this area allow it to meet even the most complex needs of medical equipment manufacturers.
Class I medical devices
The manufacturing process for Class I and II medical devices is very similar. In addition to moulding the plastic parts, these companies also need to meet rigorous quality standards and strict regulatory requirements. This consists of many steps, including the selection of engineering materials, quality management systems and cleanrooms. In addition, a high-skilled workforce is essential. In addition, the Four E's are used to define the standards that must be met in the manufacturing process.
The process and materials for producing medical devices must be standardized and adhere to ISO regulations. This process is suited to manufacturing high-volume, complex components. It is also efficient, yields excellent results, and is capable of a rapid turnaround. In addition, it offers a wide range of materials that can be used to manufacture Class I medical equipment moulds. The advantages of medical injection molding are numerous. For instance, a medical injection mold can be used for prototyping.
 +86-15995701933
+86-15995701933 [email protected]
[email protected]- OEM Plastic Mould Manufacturers

 ��������
��������