Mold casting classification
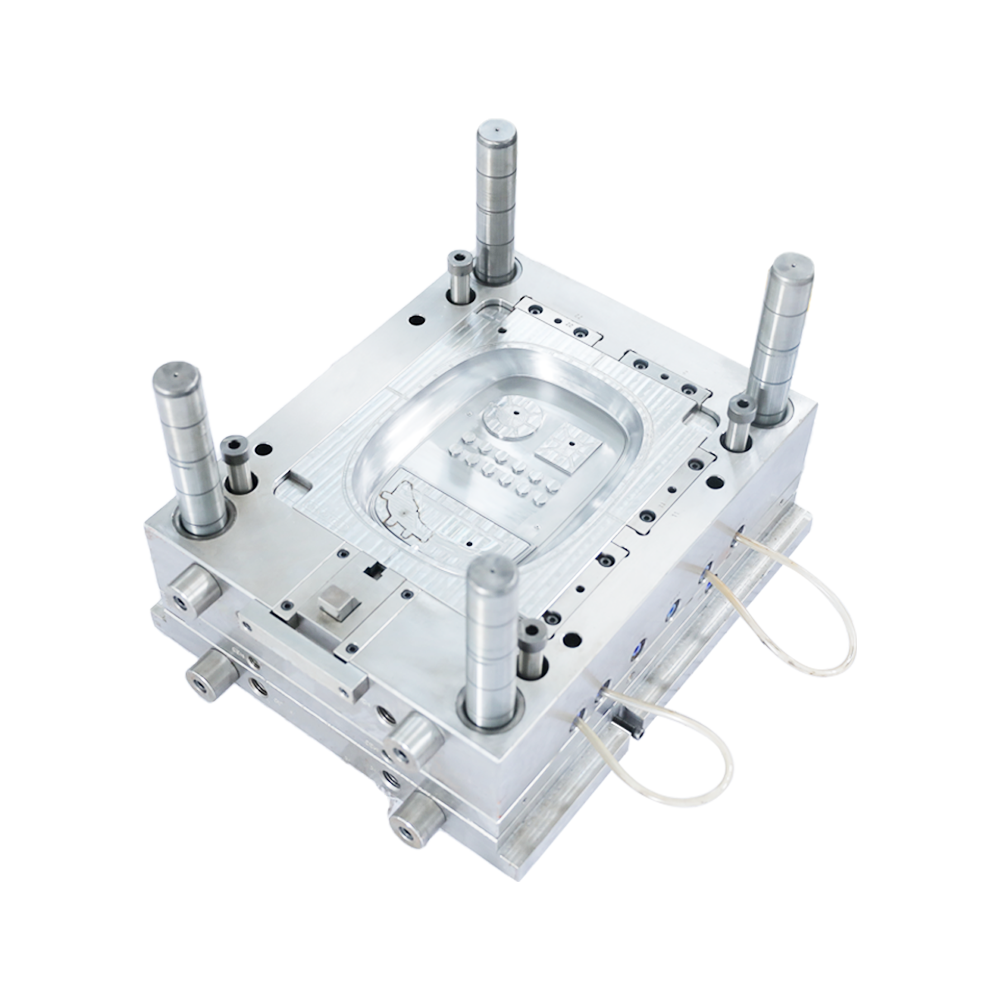
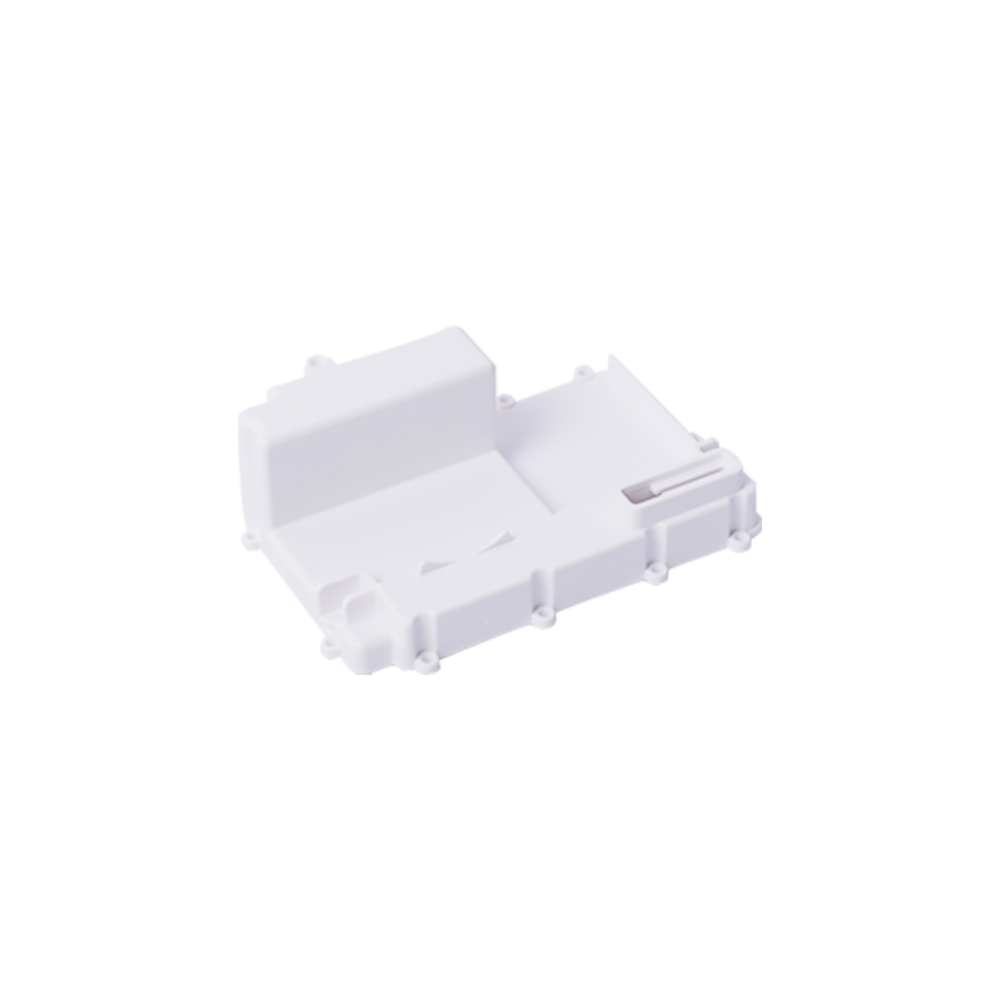
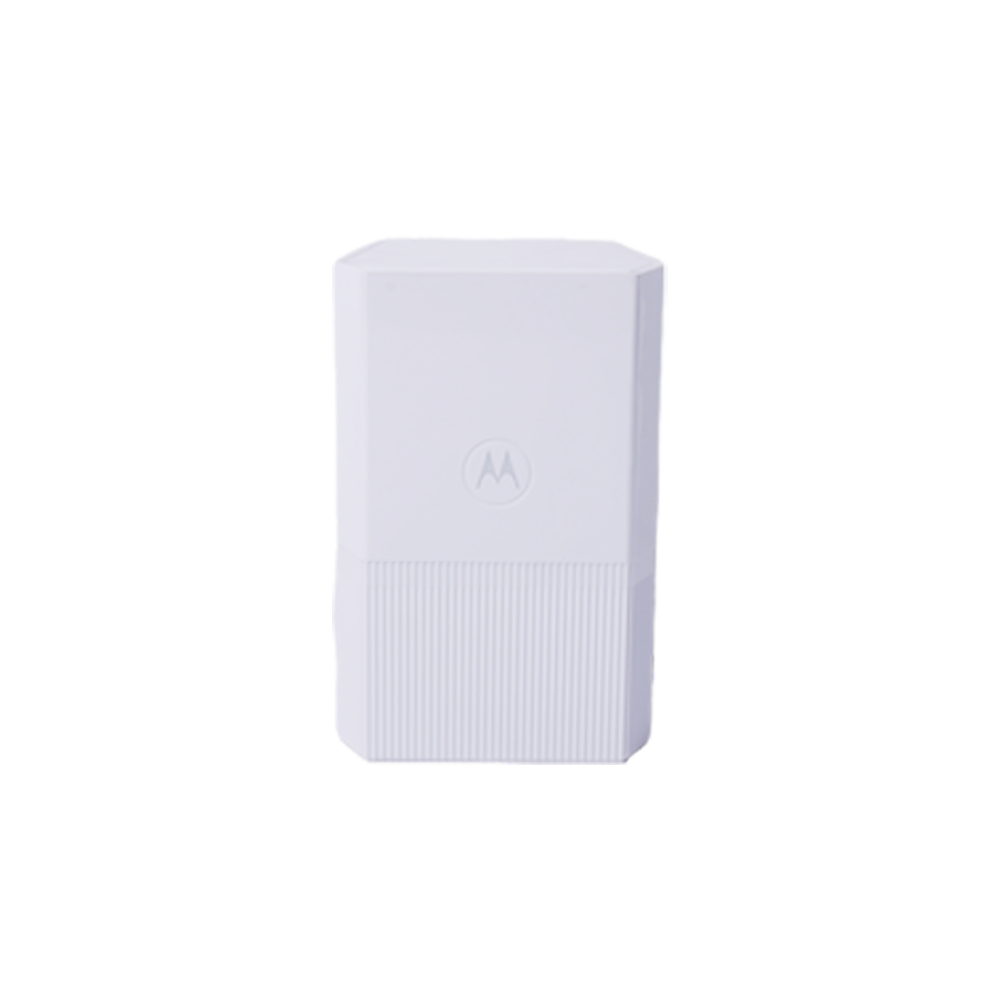
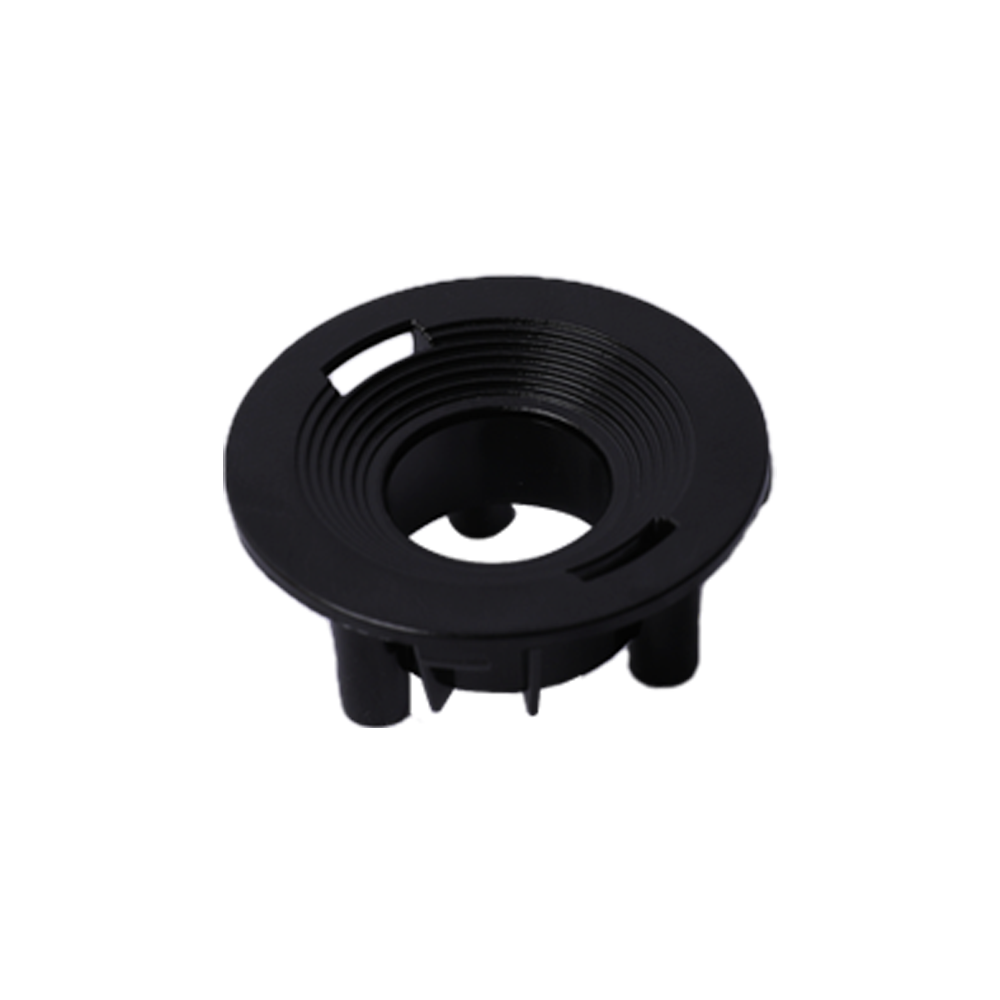
(1) Injection molding
The plastic is first added to the heating barrel of the injection machine, and the plastic is heated and melted. Under the push of the screw or plunger of the injection machine, it enters the mold cavity through the nozzle and the mold pouring system, and is hardened and shaped into injection molding due to physical and chemical effects. product. Injection molding consists of a cycle consisting of injection, pressure holding (cooling) and plastic part demolding processes, so injection molding has the characteristics of periodicity. Thermoplastic injection molding has a short molding cycle, high production efficiency, and low wear on the mold by the melt. It can mold plastic parts with complex shapes, clear surface patterns and markings, and high dimensional accuracy in large quantities; however, for plastics with large wall thickness changes. It is difficult to avoid molding defects. Anisotropy of plastic parts is also one of the quality problems, and all possible measures should be taken to minimize it.
(2) Compression molding
Commonly known as compression molding, it is one of the earliest methods of molding plastic parts. Compression molding is to directly add plastic into an open mold cavity with a certain temperature, then close the mold, and melt the plastic into a flowing state under the action of heat and pressure. Due to physical and chemical effects, the plastic is hardened into a plastic part with a certain shape and size that remains unchanged at room temperature. Compression molding is mainly used for molding thermosetting plastics, such as phenolic molding powder, urea-formaldehyde and melamine-formaldehyde molding powder, glass fiber reinforced phenolic plastic, epoxy resin, DAP resin, silicone resin, polyimide and other molding compounds, It can also be processed into unsaturated polyester dough (DMC), sheet molding compound (SMC), prefabricated integral molding compound (BMC), etc. Under normal circumstances, compression dies are often divided into three types: overflow type, non-overflow type, and semi-overflow type according to the matching structure of the upper and lower molds of the compression film.
(3) Extrusion molding
It is a molding method in which the plastic in a viscous flow state passes through a die with a specific cross-sectional shape at a high temperature and a certain pressure, and then is shaped into a continuous profile with the desired cross-sectional shape at a lower temperature. The production process of extrusion molding is preparation of molding materials, extrusion molding, cooling and shaping, traction and cutting, and post-processing (quenching and tempering or heat treatment) of extruded products. In the extrusion molding process, pay attention to adjusting the temperature, screw revolutions, traction speed and other process parameters of each heating section of the extruder barrel and the die in order to obtain qualified extrusion profiles. Special attention should be paid to adjusting the rate at which the polymer melt is extruded from the die. Because when the extrusion rate of the molten material is low, the extrudate has a smooth surface and a uniform cross-sectional shape; but when the extrusion rate of the molten material reaches a certain limit, the surface of the extrudate will become rough and tarnished , appear shark skin, orange peel, shape distortion and other phenomena. When the extrusion rate was further increased, the extrudate surface was distorted and even fragmented and fractured into melt fragments or cylinders. Therefore, the control of extrusion rate is very important.
 +86-15995701933
+86-15995701933 [email protected]
[email protected]- OEM Plastic Mould Manufacturers

 ��������
��������